摘要:在中国,风景园林往往参与到大尺度的框架规划中来。在铁岭新城中央景观系统与莲花湖生态公园这两个项目中,生态思考在规划与设计过程中扮演着中心角色。
In China, landscape architecture often involves working within a large-scale framework. During the creation of Tieling New Town’s central landscape system and Lotus Lake National Wetland Park ecological thinking was central to the planning and design process.
Article Source: Xiaodi Zheng. Think Big, Birds First. TOPOS, VOL. 77. 2011
声明:此文章为正式授权文章,已征得作者郑晓笛同意在风景园林新青年(Youth Landscape Architecture) 上发表,严禁转载。
Notice: This article is a reprinted version with the official permission of the author Xiaodi Zheng. Do not copy without permission.
In the past decade, China has been building new towns throughout the country with an unprecedented speed. The necessity to create these new urban settlements from scratch is debatable, as is the appropriateness for the new towns to take over farmland. However, this pressing reality requires practicing landscape architects in China to be capable of envisioning large- scale landscape frameworks at the city level, and also requires them to be adept at dealing with complex challenges in multiple disciplines including ecology, civil engineering, urban design, and tourism planning. During the creation of Tieling New Town and Lotus Lake National Wetland Park, the design team was required to respond to all of these challenges.

Tieling newTown.
The city of Tieling is located in Northeast China, with a population of over three million inhabitants. It is situated within a tra- ditional agricultural area that has been suffering from a slow pace of eco- nomic growth over the years. To cope with the need for fast processes of urbanization and to stimulate new industries, the local government ap- proved an updated version of Tieling’s City Master Plan in 2006. The plan envisioned a new town 13 kilometers southwest to the old city center. The identified site for this new development occupies an area of 35 square kilometers with an expected population of 300,000 in 2020. Fan River flows through the west portion of the site.
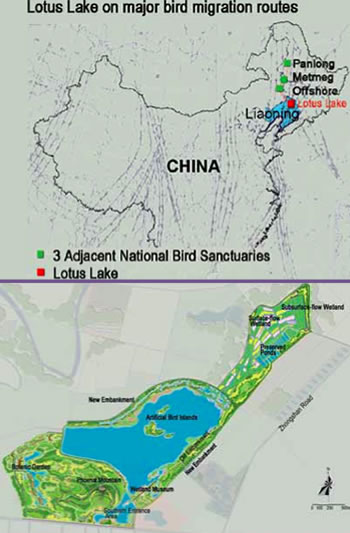
Bordering the north limit of Tieling New Town, the Lotus Lake connects to the Liao River to the north, which is the main watercourse in the region. The surrounding area was a vast freshwater marsh before rice paddles grad- ually encroached on the wetland. In the 1960s, the Lotus Lake was turned in- to a reservoir for flood detention and irrigation supply. Following years of sedimentation and pollution, the lake’s open water area shrunk to 2.3 square kilometers, with an average depth less than one meter. However, it still serves as an important habitat for a variety of fauna and flora species.
In Tieling’s 2006 City Master Plan, Shanghai Tongji City Planning & Design Institute defined the New Town’s basic layout and set a 3.1 kilo- meter water corridor, Tianshui Canal, as its north-south central axis, which connects the Fan River on the south with Lotus Lake on the north. Shortly after, the Department of Landscape Architecture at Beijing Tsing- hua Urban Planning & Design Institute (THDLA) was invited to conduct an in-depth planning and design of the central district of the New Town, including the Ruyi Lake serving the administrative core, the axial water- course bisecting the central business district, and Fengguan Mountain anchoring the north end of the water axis.
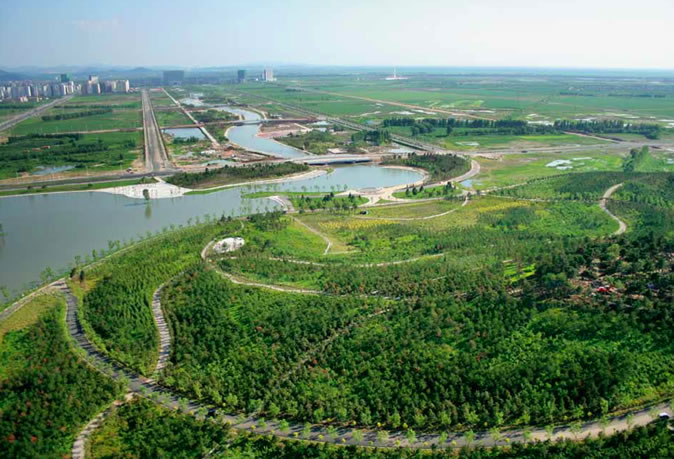

“It is critical for landscape architects to get involved at city planning stage to ensure that things are done right at the bigger scale, rather than just filling in the gaps between buildings in a later time” states Jie Hu, chief de- signer at THDLA, “This is especially true during the creation of new towns and new cities in China.” Based on the design by THDLA, each main land- scape element in the New Town was given a unique identity: the Ruyi Lake in front of the new government buildings displays a political image and is activated by the retail district and recreational amenities; the central water- course and its adjacent parkland provide a variety of outdoor spaces for local residents; and Fengguan Mountain, together with Lotus Lake, serve as habitat rehabilitation zones and protected wetland park.
Ecological and sustainable design approaches are taken into consider- ation at the planning stage and carried through all the way to the con- struction of the landscape systems. Based on computer simulation mod- els, two main issues are tackled: to direct water from Fan River through the central watercourse to solve the water shortage problem at the Lotus Lake; and to incorporate a series of constructed wetlands to purify dis- charged water from the old city center before it enters the Lotus Lake and eventually the Liao River. On average, 60,000 tons of treated water supple- ments Lotus Lake now daily through a 67 hectare constructed wetland composed of subsurface-flow and surface-flow wetlands.
Lotus Lake national Wetland Park.
Lotus Lake functions as an impor- tant stop along the East Asia Bird Migratory Route, and provides habitat for 165 bird species, including 18 endangered species. To protect this important habitat, the Lotus Lake and its surrounding area of 47 square kilometers were designated as National Wetland Park in 2006. The first phase of restoring its core area of 629 hectares was carried out by THDLA, and construction was already completed in 2008.
The design of the Lotus Lake Wetland Park was influenced greatly by two research projects. The first one was an environmental impact study that examined the possibility of relocating the old embankment and en- larging the water surface of Lotus Lake, and it was conducted by the De- partment of Environment at Tsinghua University. The second research project was about the required bird habitats in the region, and it was car- ried out by graduate students at the Department of Landscape Architec- ture in Tsinghua University. The bird habitat study provided a nice bridge between students’ academic research and professional practice. The stu- dents gained an opportunity to observe the complicated conditions asso- ciated with design challenges in real world, and to investigate the relation- ship between ecological preservation and recreational needs. At the same time, their research provided valuable information for the design team.

Based on accumulated observation data over the past 20 years, the research team analyzed the types of birds in the study area and their respective habitats. Six groups of birds are categorized according to their dependency on the aquatic environment, as well as their behav- ior characteristics. According to the birds’ needs, was concluded that four types of habitats were in shortage, including woodlands, bushes, bulrush marsh, and shoal.

Throughout the design process of the Lotus Lake National Wetland Park, priority has been put upon the ecological systems and bird habitat needs over human recreational desires. For example, three islands with bulrush marsh areas were created only for birds. Originally, the City Master Plan required re- moving the old lake dyke to enlarge the water body for a grand gesture and irrigation needs. During the design phase, the landscape architect and the re- search team found out that the old dyke holds the only existing woodland habitat for the majority of the migratory birds. They were able to convince the local government to preserve the old dyke and build another layer of new dyke outside of the lake to increase overall water storage volume. After mak- ing sure that all ecological requirements were met, the design team added a layer of recreational pathways and educational facilities selectively through the site. No human activities are allowed in sensitive and fragile habitat zones, while opportunities are provided for visitors to observe, to learn about, and to appreciate both the migratory and non-migratory birds in the park.

From 2006 to 2008, the landscape framework of Tieling New Town, to- gether with the first phase of Lotus Lake National Wetland Park, was taking shape from design to built realities. It is exciting, but at the same time it can be horrifying, to see such fast construction at the city scale. Wouldn’t it be more sustainable to use all of the money and effort to improve urban envi- ronments of existing city centers and to preserve more farmland? However, when the strong political wheel has set its course, we, as landscape architects, at least can try to make things right and use it as an opportunity to correct past mistakes. Because the relatively low cost of landscape projects compared to architecture projects, and the “instantly greened” image that landscapes can provide, along with the increased land value they can stimulate in the adjacent region, it is becoming common practice in China to implement the central landscape area first during the creation of new towns and new cities. It is imperative for the landscape architect to have a voice at the planning stage, or more ideally, to act as the project leader. To be prepared to fulfill this role, landscape architects need to train themselves to think at a regional scale, and to obtain a synthetic understanding of multi-disciplinary know- ledge, including civil engineering, water treatment technologies, ecological rehabilitation, simulation tools, GIS analysis, and the arts. Last but certainly not least, landscape architects must be able to convey ecological design thinking to the government officials in a convincing manner.
LOTUS LAKE NATIONAL WETLAND PARK, TIELING, P.R.CHINA
Client: Tieling City Planning Bureau
Landscape architects: Department of Landscape Architecture at Beijing Tsinghua Urban Planning & Design Institute (ThDLA)
Construction: 2008
Area: 6.29 square meters Cost: 17.5 million US dollars
这到底设计啥了?种了一片朴野植物就OK了不是么?
您是没看文章只看了个图片吧?
请教一下,问什么要把国家城市湿地公园的名号改成生态公园呢,如果是这样的话,该怎么区分生态公园和城市湿地公园?
请教一下,问什么要把老鼠叫成耗子呢,如果是这样的话,该怎么区分老鼠和耗子?