编者按:风景园林设计虽然经常牵扯到社会、经济、生态、艺术等多方面的因素,但似乎总是与政治无关,而本文则为我们讲述了一个发生在西班牙马德里的,作为政治选举手段的设计项目的曲折故事。
Article Source: Christian Dobrick. Madrid Rio; Landscape architecture as a political means. TOPOS, VOL. 73. February, 2011.
声明:此文为正式授权文章,已征得作者同意在风景园林新青年(Youth Landscape Architecture)上发表,严禁转载。
Notice: This article was first published in TOPOS, it is a reprinted version with the official permission of the author Christian Dobrick and West 8 urban design & landscape architecture. Do not copy without permission.
The masterplan for a 120-hectare site of a reclaimed riverbank and a new urban area in the Spanish capital is based on a trilogy of key areas that provide the basic structure: a riverwalk, a large park and a project to rebuild an urban ensemble. The interventions are to restore the urban fabric.
Architecture is a discipline concerned with concepts and design. As afield strongly associated with ideological and political goals it often is the subject of criticism. Many historic examples of Haussmannian proportions spring to mind. Landscape architecture, in contrast, presents itself as an innocent profession, immaculate and almost politically neutral. That is because the profession’s design elements are exclusively associated with positive aspects of nature. They are not linked with political leanings. To devise a concept for the mayoral elections of2003 in Madrid, Alberto Ruiz Gallardón used his political experience to instigate an infra-structure development project in Madrid. His ambitious proposals included the construction of more than 100 new metro stations, improvements to 43 km of orbital motorway and the development of four high-rise buildings, which would define the city’s skyline. His election campaign focused on infrastructure measures to help strengthen fundamental conditions for a thriving economy, placing the emphasis on improvements to housing and the public realm within the city. The target was to accomplish basic structural renewal for the benefit of future generations. The citizens supported Gallardón’s plans with an absolute majority, in spite of the concurrent rise in taxes to finance the projects. In the time leading up to the financial crisis, the mayor implemented the six-billion euro infrastructure development as promised within his four-year term in office. Consequently, parts of the city centre were transformed into a permanent construction site with traffic congestion reaching almost intolerable levels. In the centre, where six km of Madrid’s urban motorway were to be aligned below ground, a 120-hectare hole was dug close to the old town. At the end of the legislative period, Alberto Ruiz Gallardón had delivered his program, and a large percentage of the population expressed confidence in him. The relationship of cause and effect of the promised interventions with the financial reality and the people’s trust in an individual is unimaginable in this form in most European countries. During the construction phase of the tunnel, an international invited competition for the design of the open space on top of it was launched. The landscape architects and urban designers West 8 from Rotterdam together with a group of renowned architects from Madrid, united under the name MRIO arquitectos led by Ginés Garrido Colomero won the competition with their masterplan design for a reclaimed river bank and a new urban area.
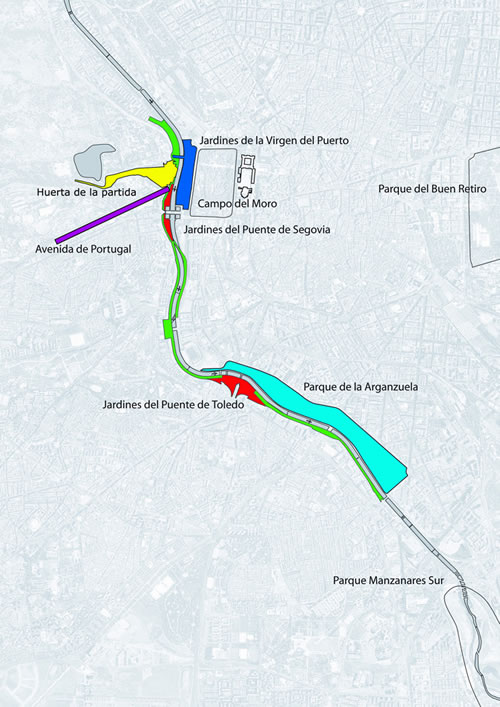
01: Photo Credit: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture
The competition proposal is based on the 3+30 concept, founded on the idea that the 120-hectare site is developed in a trilogy of key areas that provide the basic structure: a riverwalk along the Manzanares, a large park and a project to rebuild an urban ensemble, which had been severed by the orbital motorway near the royal palace in Madrid. A series of public and private interventions were to restore and enhance the urban fabric. The sections of the project completed in time for the elections in 2007, Avenida de Portugal, Huerta de la Partida and a part of the Salon de Pinos riverwalk covered only five percent of the total site area. At the official opening of Avenida de Portugal, the mayor explained his aspiration for a concurrent development of the economy and amenity value, using the ex-ample of the new green open space on the roof of a four-lane motorway and an underground car park for 1,000 cars. After his re-election the mayor decided that all of the competition proposals should be realized within his second term in office, and he allocated a total budget of 280 million euros. Again, the project was to be financed with a loan from the municipality and repaid by the citizens over 30 years. According to Gallardón, investment in open space would repay in the long-term through improvements to the quality of the urban environment. He deliberately avoided building development on the site to help refinance the project. The design phase of the 47 sub-projects coincided with the onset of the financial crisis, which hit Spain’s construction sector particularly hard. The 80 hectares of land above the tunnel were covered with a thin layer of soil and left a visible scar within the city. At the time when the parks, boulevards and plazas were scheduled for construction, the crisis reached its peak. Implementation was cast into doubt due to the slump in income from public finances and the suspension of building projects. To honour the promise that the open spaces along the river should be completed before the elections in the spring of2011,the city decided to use grants from the so-called Plan E, the national program for subsidising the economy, to implement the work. This decision meant that construction could continue without delay and the architects were confront-ed with even tighter time schedules. Projects had to be subdivided into smaller sections to meet the criteria of the grants, which were specifically aimed to help medium-sized construction companies.
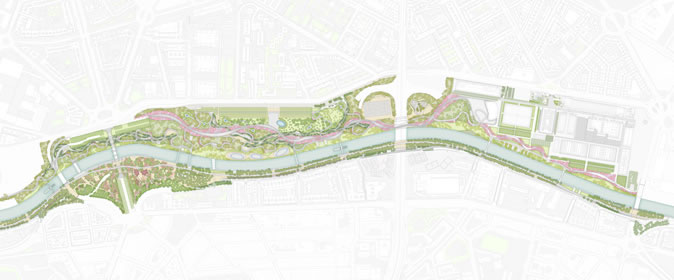
02: The plan highlights the Arganzuela Park on the northern bank of the river. The park is the largest section of the project covering 40 hectares. The river gardens near the Puente de Toledo in the west are currently under construction. Photo Credit: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture
Salon de Pinos was opened in 2010.It is the project’s backbone, designed as a linear open space along the River Manzanares, which links existing and new urban green spaces. The theme for almost the entire area of the tunnel cover is the vegetation from the mountain region close to Madrid. Pine was chosen as the dominant species and 8,000 specimens of this resilient tree which thrives on were rock planted. The choreography of tree planting, using a pallet of pruned and shaped specimens as well as mixed and sloped planting, lent the site a natural and sculptural character, and created a botanical monument. Recently completed bridges link the Salon with the site of the proposed Arganzuela Park. In contrast to other footbridges, the two parallel bridges “Puentes Cascara” provide a shady space above the cool waters of the river, and they offer views to the city. The bridges are shaped like rough concrete domes with more than 100 thin steel cables supporting their decks. The filigree detailing of the interior is only visible on the in-side The dome-like superstructures are clad in a mosaic by the Spanish artist Daniel Canogar. The bridges are more than a part of the infrastructure – they are design elements in the park. Water is the theme of Arganzuela Park, which will constitute the largest section of the project covering 40 hectares. In contrast to the canalized river flowing deep and unreachable in its engineered bed, the park takes up the different moods of the landscapes on the Manzanares and lets visitors experience the element water. A system of streams flows through the park, and the topography is used to define spaces of different characters at their junctions. Each stream has a different character: “Rio seco”, for example, is an interpretation of dry riverbeds in the Spanish landscape, where the presence of water can be felt in all seasons. Numerous plant species help to structure the space and evoke different moods. The last sections to be implemented are the hedge gardens near the historic Toledo Bridge, Arganzuela Park and Virgen del Puerto in the north. The contract program will end with their punctual opening in April 2011, immediately before the mayor’s elections. This begs the question of what the voters might think of the politics of construction in these crisis-ridden times and how future generations will perceive the implemented measures.
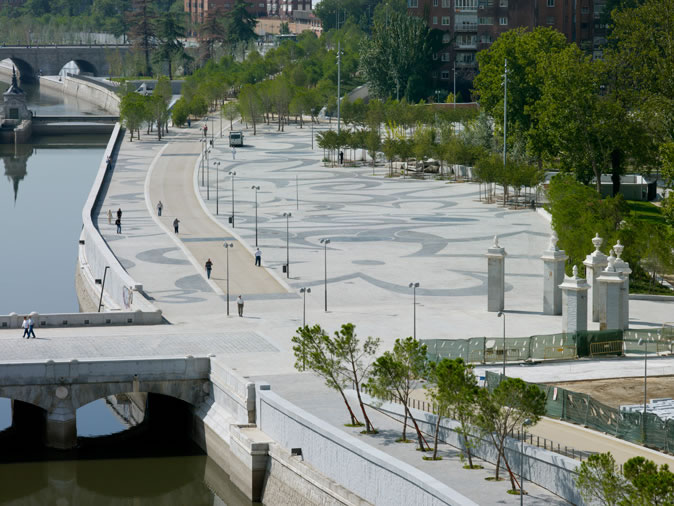

03: The paving pattern of the reconstructed Plataforma del Rey. Photo Credit: Jeroen Musch
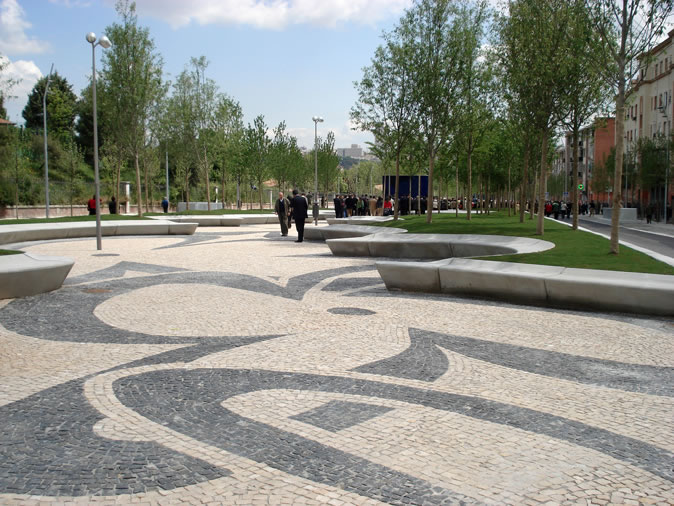

04: The paving pattern of the Avendia de Portugal reminds of cherry blossom petals. 700 cherry trees grow in the raised lawn along the avenue, which was opened in 2007. Photo Credit: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture
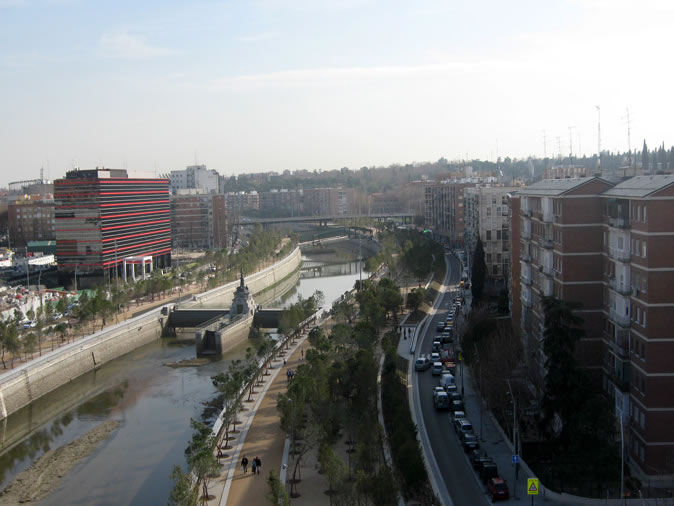

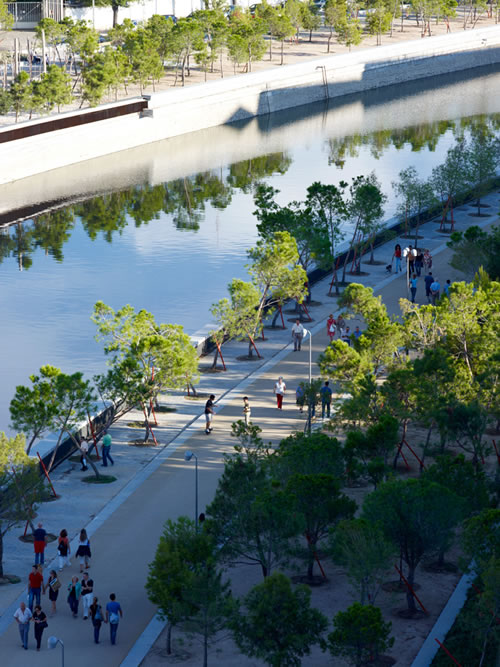
05: The Salon de Pinos comprises vibrant boulevards on both sides of the River Manzanares and is the backbone of the whole project. It opened in 2010 and now links existing and new urban green spaces.
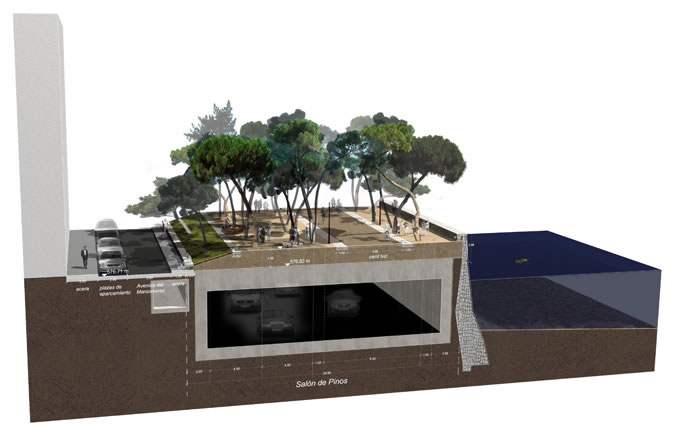
06: In their design of the riverwalk on top of the tunnel, West 8 and MRIO arquitectos interpret the vegetation from the mountain region close to Madrid. Pine was chosen as the dominant species. Photo Credit: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture

07: In their design of the riverwalk on top of the tunnel, West 8 and MRIO arquitectos interpret the vegetation from the mountain region close to Madrid. Pine was chosen as the dominant species. Photo Credit: Jeroen Musch
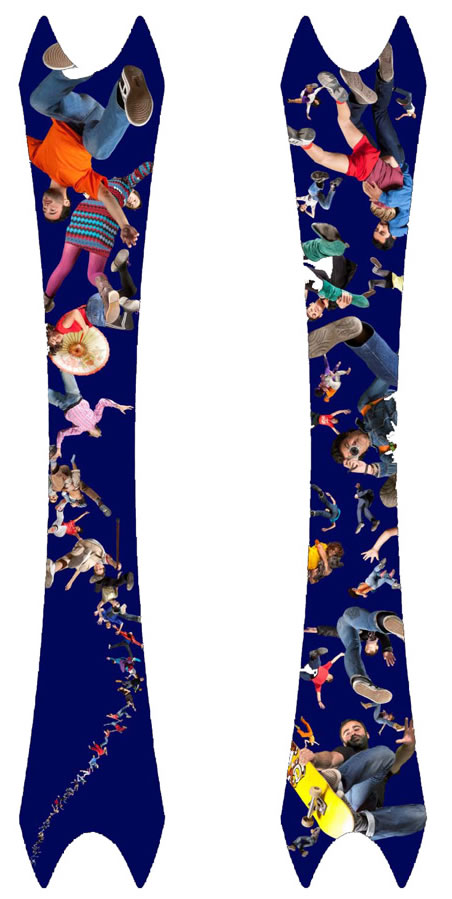

08: The interiors of the dome-like structures of the two parallel bridges “Puentes Cascara” are clad in a mosaic by the Spanish artist Daniel Canogar. The mosaic patterns show people of the neighbourhood.
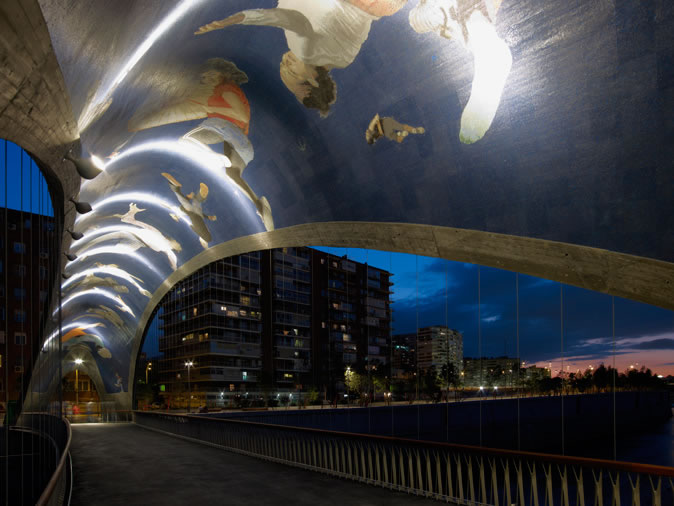

09: The “Puentes Cascara” connect the Salon the Pinos with the Arganzuela Park. Lighting along the edge of the rough concrete dome illuminates the artwork and the deck by reflection. Photo Credit: West 8 urban design & landscape architecture
想看一些国外大学上景观设计看得书,想看一些英文原版的书,但不知道看什么,有推荐吗????????
编者按:风景园林设计虽然经常牵扯到社会、经济、生态、艺术等多方面的因素,但似乎总是与政治无关
在欧洲,风景规划也好,风景设计也好都是与政治有关的
能否进一步解释呢?或者举几个实例?
文中第一段就与编者的话有些出入了,现在的人比较浮躁,看到是英文原文估计不会去看了吧。原文是指景观设计这一行业经常与意识形态和政治挂钩,相反是设计师本身不会有政治倾向。
Architecture is a discipline concerned with concepts and design. As afield strongly associated with ideological and political goals it often is the subject of criticism. Many historic examples of Haussmannian proportions spring to mind. Landscape architecture, in contrast, presents itself as an innocent profession, immaculate and almost politically neutral. That is because the profession’s design elements are exclusively associated with positive aspects of nature. They are not linked with political leanings.
第一句话说的是建筑设计,而不是风景园林,第二句才说到风景园林,而且说其是个与自然挂钩的专业,并不与政治挂钩…
haha
证明我也是比较浮躁的人,上班时偷偷的写留言
修心修心…
国内的所有政绩工程。。
由于政治体制的原因,市镇级候选人或已当选的为了获得选民的支持,通常会在下次选举前推出一些吸引选票的行为,如进行城市规划项目,旧城改造或景观项目推动经济,旅游和就业。
例子比比皆是,比较有名巴黎的公园贝西,拉维特公园,以及近几年的JARDINS DE L’IMAGINAIRE都是此类。近期法国的市镇规划项目比较多,也是为了两年后的市镇级选举的准备